CBM in Numbers
Overview of CBM Reach in 2022
8.8 million people received comprehensive support in CBM's core areas: medical aid, education and rehabilitation. This represents an increase of 3.3 million compared to the previous year. Ophthalmic care is particularly close to CBM's heart. It has reached more than 7 million people - an increase of 54 per cent compared to 2021.
For instance, ophthalmologists in CBM-supported projects performed more than 494,000 eye surgeries, e.g. on cataracts, saving the eyesight of many people. In addition, 489,000 pairs of glasses and visual aids were distributed, a simple aid with a big impact.
For more than a century, CBM has championed the rights and needs of persons with visual impairments and disabilities, ensuring that they have access to important services and opportunities. Thanks to the support of our donors and partners who share our vision, we have achieved financial stability that allows us to continue to change the lives of children and adults with disabilities for the better.
Let us take a look at the impact CBM made in 2022:
1. Eye Health
In 2022, CBM provided eye care services to 7 million people, including 494,000 eye surgeries, of which 323,000 were cataract surgeries. We also distributed 489,000 pairs of glasses and visual aids through the Inclusive Eye Health Initiative. CBM's projects helped children and adults with visual impairments to regain their sight so that they can continue their education and improve their quality of life.
-
7,029,571 people received vital eye care services.
-
494,821 eye surgeries were performed, including 323,275 cataract surgeries and 7,051 on children.
-
489,303 eyeglasses and vision aids were distributed, improving vision for hundreds of thousands.
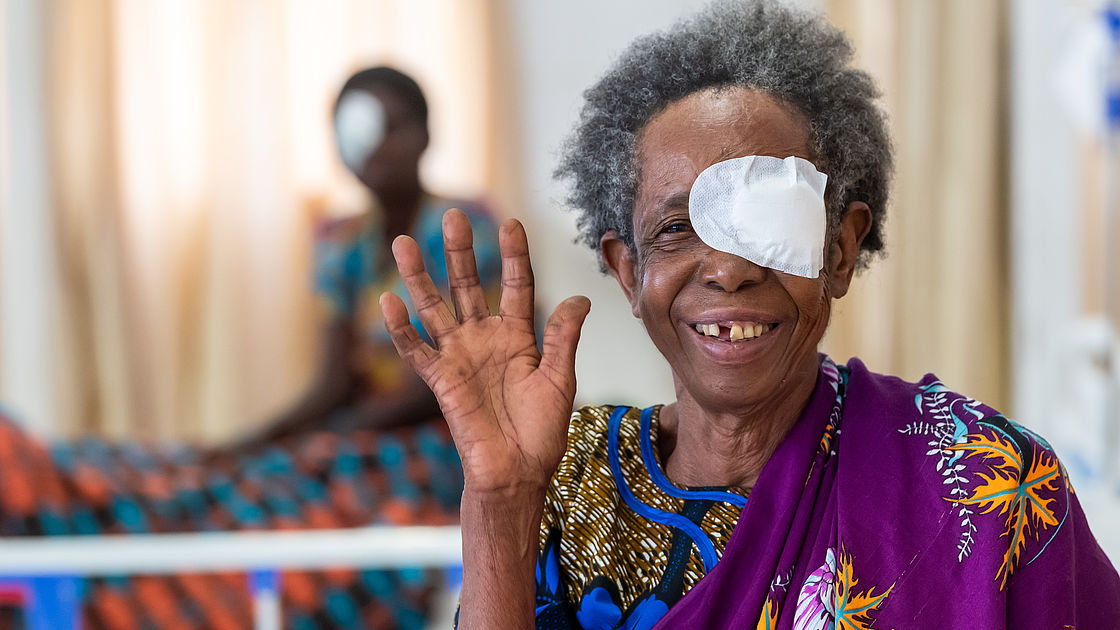
Julienne from Rwanda was completely blind when she was discovered by the outreach team supported by CBM. She underwent surgery at Kinazi District Hospital in Kinazi District, Rwanda and can now see.
©CBM/argum/Einberger2. Humanitarian Action
CBM provided humanitarian assistance to 271,215 people, including basic medical care, food, cash and vouchers, and non-food items. CBM's Inclusive Humanitarian Action Initiative ensured that persons with disabilities, who are often overlooked in emergency situations, received immediate support to help them cope with the crisis and improve their living conditions.
-
271,215 people received crucial humanitarian assistance.
-
151,689 individuals received basic medical care.
-
37,666 people received cash and vouchers, primarily used for purchasing food.
-
62,194 individuals received food support.
-
30,985 people received non-food items.
-
2,848 people with disabilities actively participated in humanitarian action projects.

Monsoon floods ravaged large parts of Pakistan in September 2022, CBM was part of the emergency response team in collaboration with Sindh Institute of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Hyderabad.
©CBM/Jamsyd Masud3. Community-Based Inclusive Development (CBID)
Through the CBID initiative, CBM enrolled 885,166 persons with disabilities in inclusive development projects. We have provided skills and business training, facilitated employment opportunities, and offered financial services to support livelihoods and promote the inclusion of persons with disabilities in their communities.
-
885,166 persons enrolled in CBID services, promoting inclusivity and livelihood security.
-
48,411 individuals received skills and business training.
-
58,035 people obtained employment, fostering equal opportunities.
-
58,941 individuals gained access to financial services, empowering economic independence.

4. Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)
CBM treated 53.5 million people for Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs), such as river blindness and trachoma, through mass drug administration, hygiene training and surgical interventions. By focusing on these neglected diseases, CBM prevented blindness and improved the overall well-being of communities at risk.
- 48,674,438 individuals received medications for eye-related NTDs.
- 29,888 participants received hygiene training to protect against NTDs.
- 16,487 surgeries were performed to prevent trachoma-related blindness.
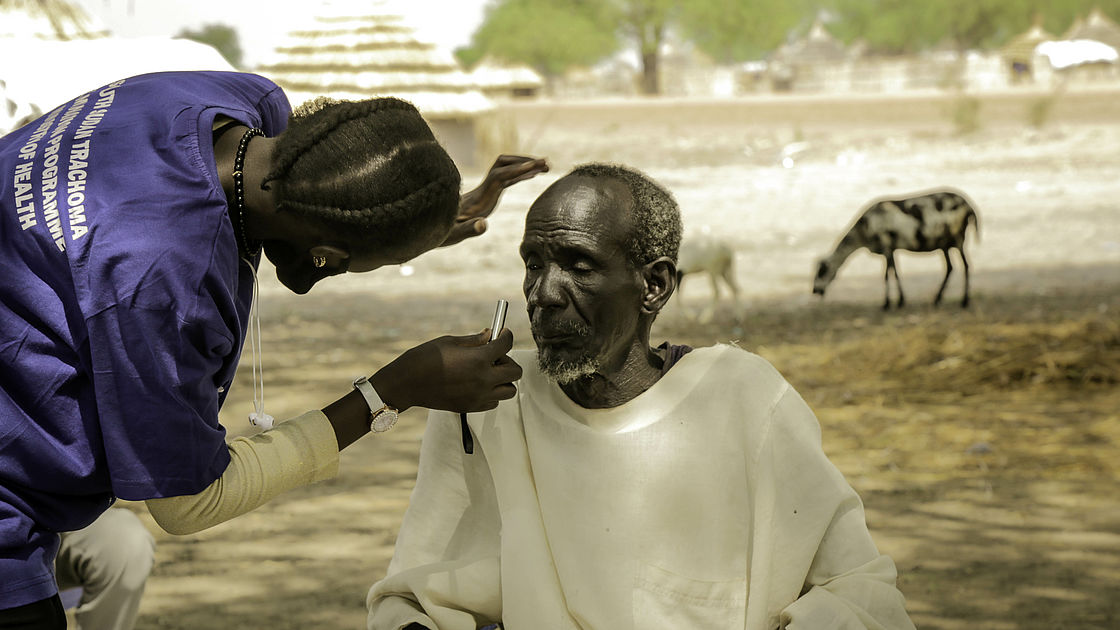

Adut Maker Noon, 21 years old, Trachomatous Trichiasis Surgery Case Finder in South Sudan examines a patient.
©CBM5. Physical Disability
CBM provided medical care and treatment to 121,894 persons with physical disabilities, including 24,225 surgical procedures. We also provided physiotherapy, orthoses, prostheses and mobility aids to improve the mobility and independence of persons with physical impairments.
-
121,894 individuals received medical care and treatment for physical disabilities.
-
24,225 surgical procedures were performed, including 4,675 on clubfoot.
-
177,556 physio or ergo therapeutic treatments were provided.
-
13,509 orthoses or prostheses and 18,066 mobility aids were distributed.
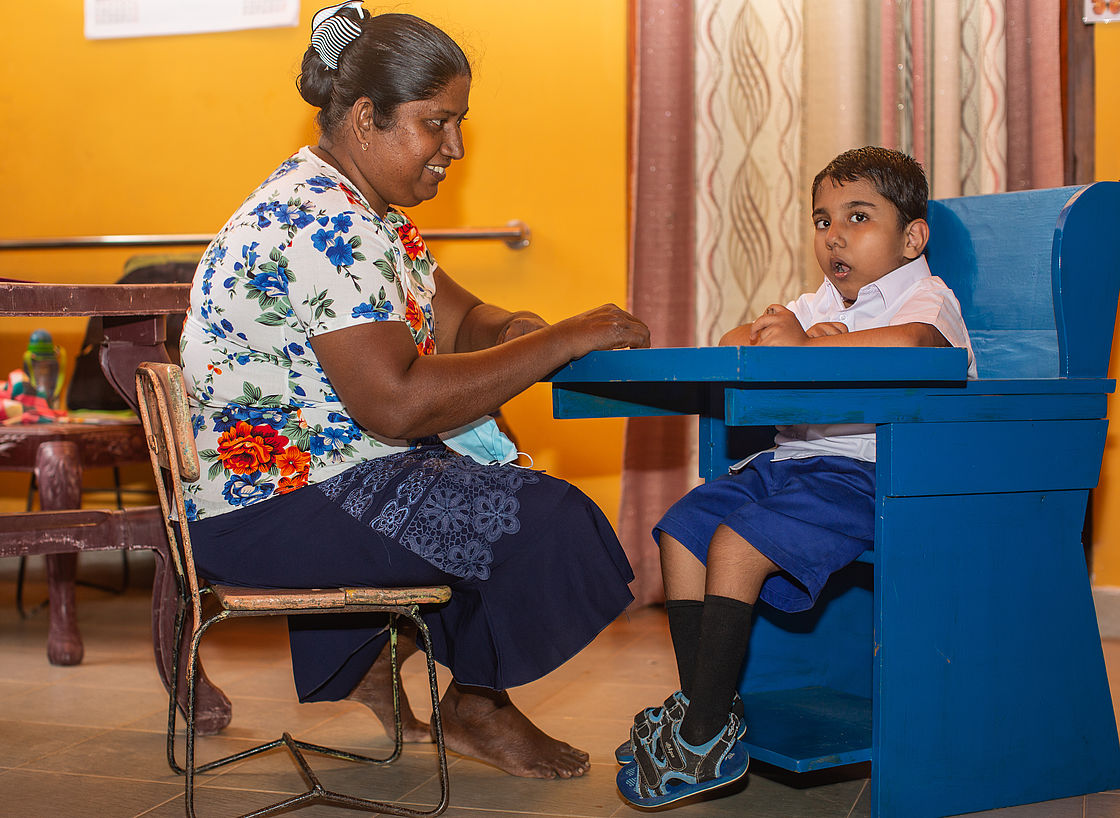

Eight-year-old Sandaruvan who has cerebral palsy lives with his mother Nimasha in southern Sri Lanka.
©CBM/Jayawardena6. Ear and Hearing Care
CBM delivered medical services to 408,703 people with ear conditions and provided speech and language therapy, hearing tests, ear surgeries and hearing aids. These measures were aimed at repairing hearing damage and promoting communication among people who are deaf or hard of hearing.
-
408,703 persons received medical services for ear conditions.
-
3,962 speech and language therapy sessions were conducted.
-
49,439 audiograms and other hearing tests were performed.
-
8,133 ear operations were carried out.
-
2,444 hearing aids and amplification devices were dispensed.
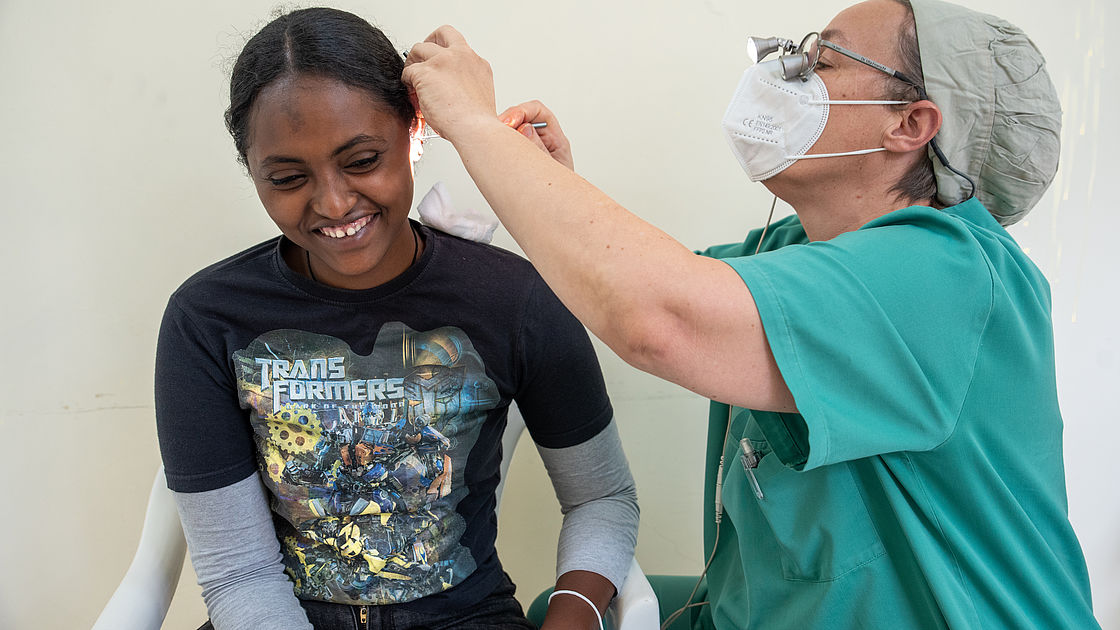
Hana (18 years) was examined after an ENT operation at the GTM hospital, a partner of CBM in Ethiopia.
©CBM7. Education and training for strong health systems
Promoting medical education and training is important to sustainably improve local care for persons with disabilities in developing countries and to prevent disability. In 2022, 16,443 people completed further training in ophthalmology, for example as ophthalmologists and optometrists. This is more than five times as many professionals as in the previous year - a big step towards strengthening local health systems.
-
16,443 participants completed training in eye care.
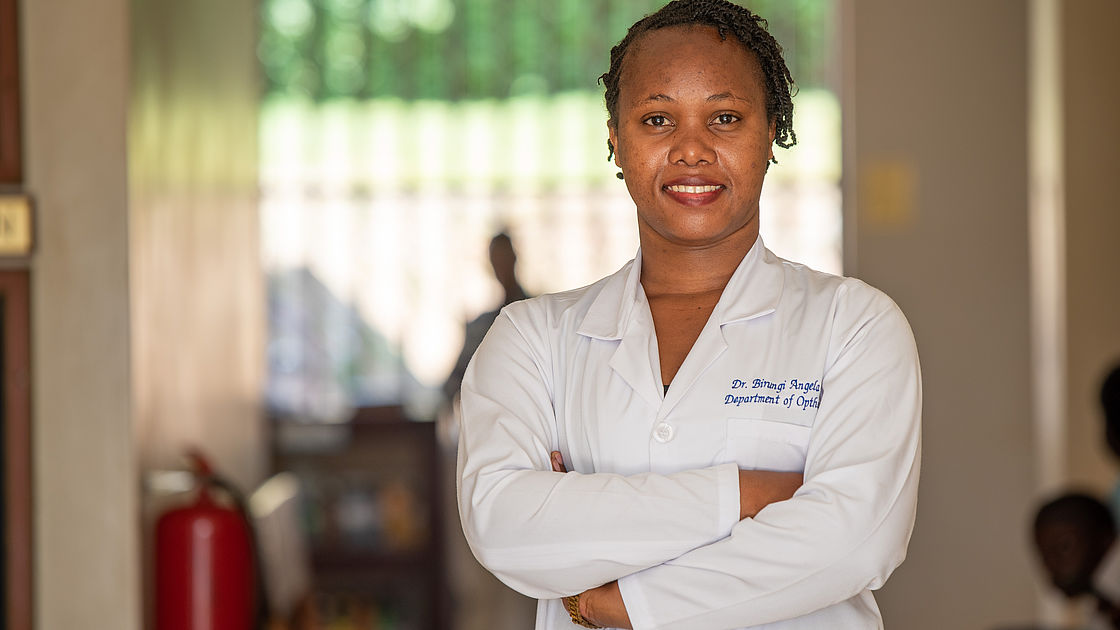

CBM Scholarship Programme: Dr. Angela Birungi is one of the ophthalmology scholarship holders currently training at Mbarara University of Science and Technology in Uganda.
©CBM